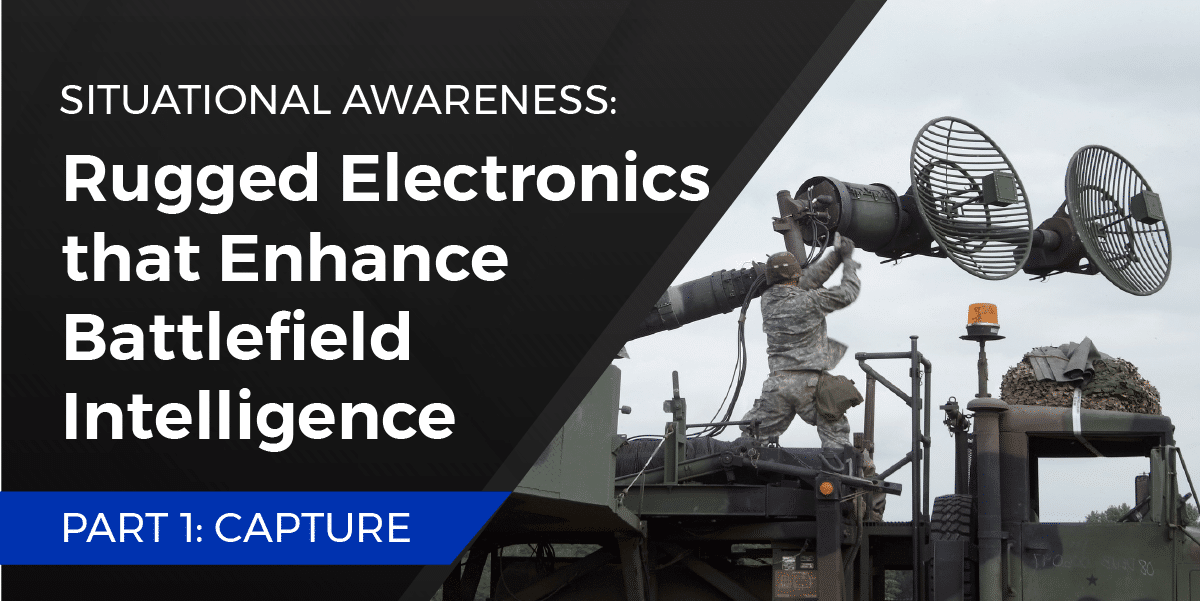
Situational Awareness: Rugged Electronics that Enhance Battlefield Intelligence - Part 1: Capture

Situational Awareness: Rugged Electronics that Enhance Battlefield Intelligence – Part 1: Capture
What is situational awareness?

In the defense world, this intelligence is often provided and enhanced by technology—from tracking the position of friendly and enemy forces, to analyzing terrain, vehicle diagnostics or even weather conditions. This process consists of a system of devices and technological capabilities that allow intelligence to be captured, viewed and distributed—all in the name of enhancing situational awareness.
In this first blog of our three-part series, we will focus on the first step in this system, capture.
Part One: Capturing Information
Before intelligence can be interpreted by operators on the battlefield, it must first be collected. Technology has revolutionized the way this information is captured, and thanks to sensors, drones, radar and more—threats can often be identified in real-time and without risking the lives of soldiers.
Cameras and Sensors
Military vehicles are often equipped with advanced cameras and sensors to provide the crew with a 360-degree view of the surroundings. These cameras go beyond the standard video feed, with the ability to capture moving targets and to provide thermal and multispectral imaging. And, it goes without saying these cameras are uniquely positioned to withstand demanding environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, fog, high ambient light and more.
While cameras capture visual inputs, sensors can detect a variety of factors often imperceptible by the naked eye. This can include sensors for the detection of biological threats (such as aerosolized agents), radioactive material, explosives and toxic chemicals. When used on the battlefield, either in manned or unmanned vehicles, sensors can relay when an environment may be too dangerous to risk exposure to warfighters.
Unmanned Systems
Unmanned systems are just that—unmanned, leaving soldiers out of the way of harm in more precarious scenarios. This includes aerial systems, such as drones, which have the ability to surveil large areas quickly and provide teams with a line of sight to environmental conditions and enemy locations before sending in troops.
These devices are often equipped with additional advanced capabilities, such as thermal imaging or night vision and are designed to collect intelligence without being detected.
Radar and GPS
A powerful tool for enhancing situational awareness, radar transmits high-frequency radio signals to detect personnel and vehicles. These surveillance tools can scan 360 degrees every second to provide a detailed picture of movement within a set perimeter. As with cameras, MIL-Spec radar systems are designed to perform despite any extreme weather or lighting conditions.
As important as monitoring friendly and enemy force positions is, monitoring one’s own movements is critical to enhancing situational awareness and making informed decisions. GPS aids in this process by providing real-time updates on position changes and navigation.
A Full System Approach to Situational Awareness
The tools that allow intelligence to be captured, viewed and distributed on the battlefield work together to enhance situational awareness. Follow along with this series to explore how this system works together to maintain safety and ensure mission success.
Photography credit: US Army
3 Key Design Considerations When Choosing a Rugged Display

3 Key Design Considerations When Choosing a Rugged Display
When designing displays for defense and aerospace applications, manufacturers must uniquely consider a product’s ability to withstand extreme conditions. A rugged display on the battlefield must deliver performance and remain operational despite exposure to the elements, voltage spikes, shock and much more.
Systems manufacturers must be thoughtful when designing rugged displays both at the top and sub assembly level in order to meet the conditions outlined by common military standards, such as MIL-STD 810, 1275 or 704.
At DSE, our team of engineers takes special considerations when it comes to the mechanical, electrical and software design behind our rugged displays. By applying ruggedization methods at each level, DSE rugged displays have been trusted by allied forces for nearly 30 years—operating in armored vehicles, fixed-wing aircraft and rotary craft around the world.
Mechanical Design for Rugged Displays
Whether a rugged display is in freezing arctic conditions, a desert or on board an amphibious vehicle, special considerations must be made to prevent the ingress of foreign substances, such as water, dust or sand. Unlike in traditional commercial electronics, special care must be given to the sealing techniques used in rugged displays to prevent debris from entering and destroying electrical components.

In addition to sealing techniques, additional steps must be taken in order to optimize the mechanical design of rugged displays to address thermal management and general abuse experienced in the field. Thermal modeling and component selection can reduce the risk of a product malfunction in extreme temperatures, while selecting a proper material finish, such as a hard anodized aluminum enclosure can protect a display from impact or corrosive substances.
Electrical Design for Rugged Displays
Through advanced sealing techniques and the proper enclosure design, a display is prepared to face the elements brought on by each extreme environment. But ruggedization doesn’t stop at mechanical design. Electrical design considerations are equally as important when ensuring rugged displays meet military standards and perform in adverse scenarios.
Proper electronic design also goes beyond circuits. Several considerations must be taken to reduce the negative risks associated with signal interference. This is especially important when designing rugged displays, as they are particularly susceptible to electrical noise that exhibits itself visually. Signal interference from external devices, improper cable harnesses, and/or faulty designs must be overcome to produce a stable video stream. Many of today’s digital high-speed signals must be managed exactly with perfect impedance matching from end to end. This includes designing the circuit board so video and power signals are isolated and shielding internal cables to avoid susceptibility to ripples voltage noise.
Additionally, separation of ground planes including power, digital and chassis grounds, is also paramount to signal integrity.
When managed at a system level, electronic ruggedization will protect not only a rugged display’s internal components, but also the operation of other units on board.
Software Design for Rugged Displays
With a display that is mechanically and electrically sound and ready to face any adverse environments, the final component in DSE’s approach to ruggedization is software design. This final area of focus ensures the rugged display remains operable and performs its intended function in a system.

Similarly, DSE products use checksums and acknowledgement protocols to verify accurate communication and to detect firmware corruption.
Lastly, accounting for flexibility in software design can improve the usability of a rugged display. With control over the video decoder software, DSE is able to design its products to accept a myriad of video inputs that fall outside of the standard specifications, such as VESA, SMPTE and NTSC/PAL. Whereas off the shelf video cards tend to lack the control necessary to support some video sources, DSE can build unique support for specific video sources and can adapt displays to the necessary video source, even when it is beyond expected standards.
Choosing the Correct Rugged Display
From applying advanced sealing techniques, to choosing superior components and establishing built-in-tests, DSE’s approach to rugged design combines many aspects of mechanical, electrical and software engineering in order to create rugged displays fit for aerospace and defense applications.
Throughout its nearly 30 years in business, DSE has developed dozens of rugged displays to meet these unique needs.
FHDRM
The FHDRM has come to be one of DSE’s signature rugged displays, and is integrated in defense applications across the globe, including most recently in an ISR application aboard a fixed-wing aircraft.

Its ultra-thin form factor makes it an ideal choice for critical operations that require optical performance in constrained spaces. Plus, with programmable bezel soft keys, FHDRM allows for full control of external systems or even a custom interface of internal features. The FHDRM rugged display supports HD-SDI, HDMI, DVI/VGA, RS170 (NTSC/PAL) and ranges in size from 7” to a large format 24” model that was released just last year.
More Reading:
- Putting FHDRM’s MIL-SPEC Design to the Test in a Third-Party Laboratory
- Get to Know the FHDRM Rugged Display
Typhon
At the end of 2022, DSE unveiled the Typhon, a next-generation triple panel rugged display that allows for continuous display across three 1920×1200 resolution LCDs. With a focus on situational awareness, Typhon supports 9 independent camera video inputs and gives its operator a comprehensive view of mission surroundings.
Additional communications features include on-board CANBus interface, permitting remote control and access to features like video source selection, day/night modes and video positioning.

More Reading:
MSM2
One of DSE’s most flexible rugged displays, the MIL-SPEC Monitor (MSM) Series II offers countless MIL-Spec configurations. This customizable display includes a myriad of video input options including DVI, VGA, Composite Video and DisplayPort. Additional flexibility includes the option to choose sizes ranging from 6.5” to 17” and unique enclosure finishes.

More Reading: